Another cavity?!
Consider this article a public service announcement. I really dislike seeing patients lose teeth that could have been saved.
My philosophy is simple: if a patient has a dental problem, I address it—but just as importantly, I give them the tools and knowledge to prevent future issues. Ideally, most visits after that are just for routine maintenance.
Unfortunately, I often meet new patients with teeth so badly decayed there’s little chance of saving them. Just as frequently, I see people who finally schedule a checkup—often after years away from dental care—shocked to learn they have cavities. Many assume they lost a filling, when in fact, a chunk of enamel has broken off.
So why the surprise?
Most people believe cavities are supposed to hurt.
Sometimes they do. But in the early stages, they’re usually painless.
By the time a tooth actually hurts, the cavity has likely reached a serious stage. Often, I’m deciding whether to attempt a root canal—or whether extraction is the only option. A basic understanding of dental anatomy helps explain why.
Scroll down to the illustration below.
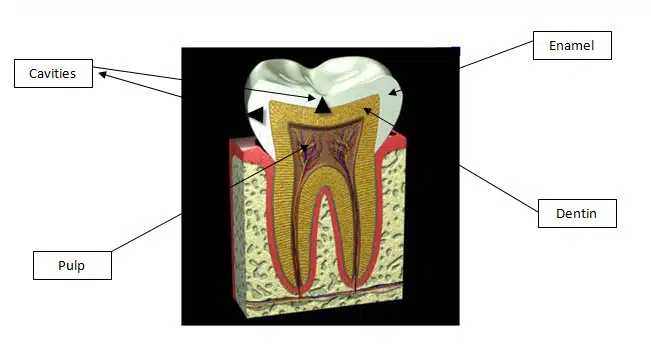
The outer layer of your tooth—enamel—is the hardest substance in your body. It’s made to last a lifetime and helps you chew your food efficiently.
But here’s the key: it doesn’t have nerves.
Enamel is more than 95% mineral. The rest is water and organic material. Because it lacks nerves, it doesn’t feel anything. That’s useful—you wouldn’t want pain every time you bit into food. But it also means decay can silently destroy it without causing any warning signs.
Even when decay reaches the underlying layer—dentin—you may still feel nothing. Only when it approaches the soft center—the pulp, where nerves and blood vessels live—do you usually feel pain. By then, the damage is often extensive.
To make matters worse, decay doesn’t spread in a straight line. Take a look at the black triangles in the diagram. A cavity often starts at a small point on the outside and fans out wide inside the enamel. The tooth might look intact—until the undermined enamel collapses due to internal damage.
Cavities also tend to form between teeth—places you can’t see. Even I need x-rays to catch them in those areas.
So what does all this mean?
Cavities don’t always show up with pain. Dentists rely on visual checks, dental probes, x-rays, and sometimes laser detection to find them. Even then, spotting decay under old fillings can be tricky.
Don’t wait for pain to tell you something’s wrong. If it hurts, the problem is already advanced—and the treatment will likely be more complex, more costly, and less predictable.
If someone you care about hasn’t seen a dentist in a while, ask them to read this article. You might help them avoid discomfort, costly procedures, and even tooth loss.
And for those thinking, “If it gets bad, I’ll just pull it,”—well, sometimes that’s necessary. But that’s a conversation for another day.
🦷 Learn more: How Cavities Form – American Dental Association