by Dr. Richard J. Walicki | Feb 4, 2026 | Dentistry
Looking for effective bruxism treatment options? You’re not alone. Millions of adults silently struggle with bruxism — and the impact on their teeth, jaw, and sleep quality can be serious. In this post, we’ll cover seven of the most common ways people manage teeth grinding — and why the right fix depends on what’s really causing it. This article outlines the most common bruxism treatment options used today, so you can better understand your choices.
🧠 Why One Size Doesn’t Fit All
In a previous blog post, we looked at the many causes of bruxism — the unconscious clenching or grinding of teeth. For some people, it’s related to stress or poor sleep. For others, it’s due to how their teeth come together, the shape of their jaw, or even the side effects of medication.
Because there are so many different causes, there are also many bruxism treatment options. Here are seven of the most common approaches that dentists and specialists may use — along with what each one is designed to address.
1. Bite Balancing
This method is based on helping your jaw rest in a natural, stable position. Some dentists use custom guides or make small tooth adjustments to reduce the pressure from uneven biting. The goal is to prevent long-term wear and reduce tension in your jaw muscles.
2. Muscle Relaxation Therapies
Some dentists and specialists use technology to track jaw movement and muscle tension. Based on that info, they guide your jaw into a more comfortable position and may use a temporary device to help you “retrain” your bite. This approach often combines dental work with physical therapy-like techniques.
3. Orthodontic Corrections
In cases where crowded or misaligned teeth are the problem, braces or clear aligners may help. Straightening the bite can reduce grinding in some people — though this isn’t always the first step unless bite problems are severe.
4. Gum and Bone Support
Some dentists believe that strengthening the support around the teeth (the bone and gums) can reduce grinding. They may focus on treating gum inflammation or tooth looseness first, especially in adults who already have signs of gum disease.
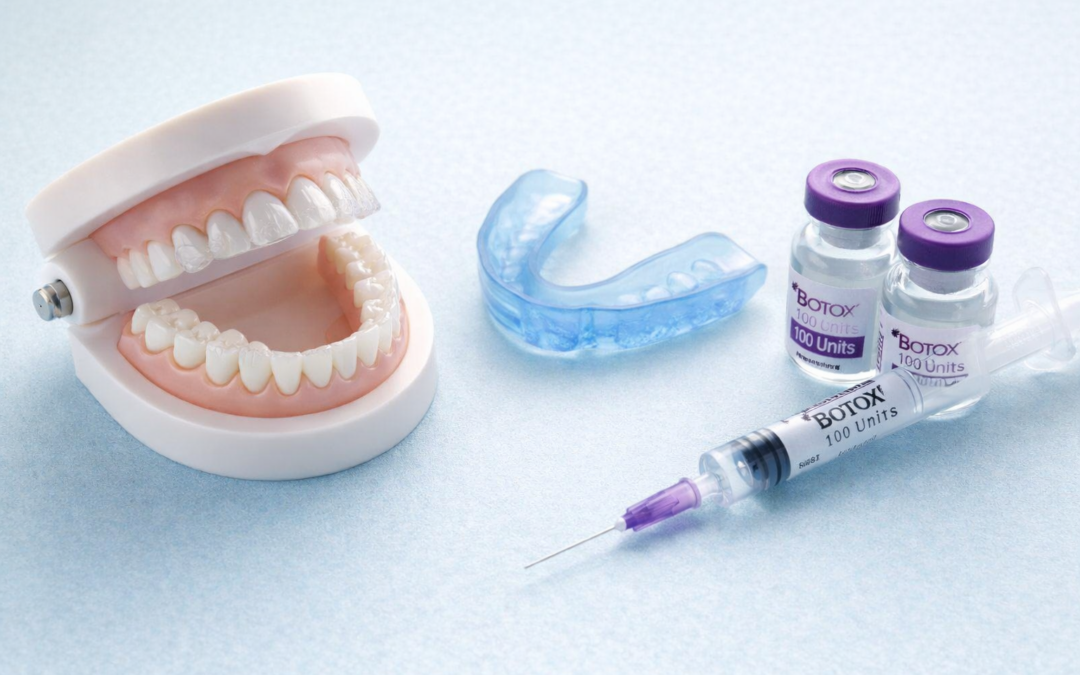
5. Botox Injections
In severe cases, small doses of Botox may be used to relax the muscles that clench the jaw. This doesn’t fix the root cause, but it can reduce pain and protect teeth from wear. Learn more from the National Institutes of Health on Botox for bruxism.
6. Custom Night Guards
Night guards (also called occlusal splints) are worn while sleeping to reduce the damage caused by clenching. These can be helpful — but only when made to fit your bite. Some dentists may also recommend special designs for patients who grind in specific directions or have other bite irregularities. The type of guard matters — and getting it checked regularly is part of proper care.
👨⚕️ Pro Tip (from Dr. Walicki):
Be cautious with over-the-counter night guards. One of my patients used one without telling me — and over time, it changed her bite so much that her front teeth no longer touched. It took full orthodontic treatment to correct it. That’s why I always recommend working with a dentist to make sure any guard fits properly and protects your teeth without shifting your bite.
7. Lifestyle & Nervous System Support
Sometimes, grinding is related to chronic stress, poor sleep, or other factors like diet, jaw tension, or medication. For those cases, calming the nervous system and supporting your overall wellness may be part of the solution — even if it doesn’t start in the mouth.
💬 Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Bruxism Treatment Options
There’s no one-size-fits-all fix for bruxism. What works for one person might do nothing for another — and in some cases, the wrong fix can make things worse.
Whether you’re just noticing symptoms or have tried treatments that didn’t work, understanding the root cause is key. Knowledge gives you the power to make decisions that protect your teeth and overall well-being for years to come.
This blog isn’t here to sell you one specific fix — it’s here to help you understand your bruxism treatment options and ask better questions at your next dental visit. Whether it’s stress, posture, airway issues, or something else — understanding your own pattern is the first step toward choosing the right bruxism treatment option for you.
If you’re exploring bruxism treatment options, this overview can help you make sense of what’s out there — and what might work for you.
Want to explore more dental insights that go beyond the basics? Visit ToothWiz.com/blog for trusted, wellness-centered guidance.
You can use one or more of these high-authority sources (just don’t mark them “nofollow” in your editor):
- Mayo Clinic – Overview of bruxism
- National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)
- Cleveland Clinic – Bruxism symptoms and causes
- American Dental Association (ADA) – Oral health topic: bruxism

by Dr. Richard J. Walicki | Jan 24, 2026 | Dentistry
Bruxism causes—commonly referred to as teeth grinding or clenching—are often discussed as though there is a single explanation. Some professionals attribute it primarily to stress. Others focus on bite alignment, muscle activity, sleep disorders, nutritional deficiencies, or even bacteria.
When people search for answers about bruxism, they are often looking for a single explanation. In reality, most bruxism causes involve overlapping biological and behavioral factors.
What’s striking is that each of these perspectives has supporting data—and each shows improvement when addressed in the right context.
Rather than being contradictory, this may point to a more accurate conclusion: bruxism is not a single-condition problem. It is multifactorial.
Why Bruxism Causes Are Rarely Just One Thing
One of the most compelling clues that bruxism has multiple contributing factors is that very different approaches can reduce or stop it. Stress reduction helps some patients. Bite adjustments help others. Nutritional support, medication changes, or sleep-focused interventions can also make a noticeable difference.
Bruxism as a Sign, Not a Diagnosis
One of the most important shifts in modern dentistry is recognizing that bruxism is best understood as a functional output, not a disease in itself.
In other words, grinding and clenching are behaviors generated by the nervous and muscular systems in response to internal or external stimuli. That helps explain why treating one contributing factor can dramatically help one patient, yet do little for another.
This also explains why long-standing debates about the “true cause” of bruxism persist—each school of thought is observing a different piece of the same puzzle.
Stress and Central Nervous System Activation
Stress-related bruxism is perhaps the most widely recognized theory, and for good reason. Elevated stress levels increase sympathetic nervous system activity, alter sleep architecture, and raise muscle tone—particularly during micro-arousals in sleep.
Multiple studies have shown associations between stress, anxiety, and increased bruxism activity, especially sleep bruxism. Addressing stress through behavioral changes, sleep hygiene, or nervous system regulation often reduces grinding intensity in these patients.
If you’re interested in how sleep-related changes can affect oral health, you may also find this helpful:
The Science Behind Morning Breath: Why It Happens and How to Fix It.
Neuromuscular and Motor Pattern Theories
Another body of research views bruxism as a neuromuscular phenomenon—a repetitive motor pattern driven by reflex loops involving the brainstem and masticatory muscles.
This perspective helps explain why certain approaches aimed at muscle regulation (including improving sleep quality or reducing physiologic arousal) sometimes reduce clenching. It also aligns with findings that bruxism can occur during specific sleep phases associated with autonomic activity.

Occlusion-Based Explanations
Historically, occlusal interferences were thought to be a primary cause of bruxism. While modern research suggests bite issues alone rarely cause bruxism, they can act as perpetuating or amplifying factors in susceptible individuals.
Correcting occlusal discrepancies may reduce symptoms for some patients—not because occlusion is the root cause, but because it reduces abnormal proprioceptive input to the nervous system.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Neuromuscular Excitability
Certain nutritional deficiencies—particularly magnesium, calcium, and B vitamins—are associated with increased neuromuscular excitability.
Clinical observations and some studies suggest that correcting deficiencies can reduce bruxism intensity in certain individuals. This does not imply nutrition is the cause of bruxism, but rather one potential contributor among many bruxism causes.
Microbiome and Inflammatory Theories
Emerging research has explored whether chronic inflammation or oral microbiome imbalance may influence neuromuscular activity or sleep quality. While this area is still speculative, it underscores an important theme: bruxism may reflect systemic imbalance rather than isolated dental pathology.
Medication-Induced Bruxism: The Benzodiazepine Connection
One of the most clinically revealing insights into bruxism emerged from studies examining unexpected dental implant failures.
Dental implants typically demonstrate long-term success rates of approximately 90–95%. However, some analyses noted a higher-than-expected failure rate in patients taking certain medications—particularly benzodiazepines.
Further investigation suggested that these medications can alter sleep architecture and muscle regulation, increasing the likelihood of nocturnal bruxism. The resulting excessive forces may overload implants, contributing to failure.
This finding reframes implant complications not as purely mechanical issues, but as interactions between biology, behavior, and systemic factors. It also supports the broader idea that bruxism causes often extend beyond the teeth themselves.
For readers who want a mainstream overview of bruxism (including risk factors and management options), these are solid starting points:
Why a Multifactorial Model Makes Sense
When stress reduction helps one patient, occlusal adjustment helps another, nutritional support helps a third, and medication review helps a fourth—the most logical conclusion is not that one theory is correct and the others are wrong.
Rather, bruxism represents a final common pathway—a behavioral response that different individuals reach through different mechanisms.
What This Means for Patients and Clinicians
Understanding bruxism as multifactorial encourages individualized evaluation, realistic expectations, and protection-focused strategies (such as night guards) rather than promises of a single cure.
If you’d like to explore other ToothWiz Health content related to grinding and clenching, you can browse here:
Search ToothWiz for “bruxism”.
The Bottom Line
Bruxism is not a failure of teeth or dentistry. It is a signal—often reflecting stress, sleep disruption, neuromuscular imbalance, systemic influences, or a combination of all four.
Recognizing this complexity is not controversial. It is simply consistent with how the human body works—and it’s often the most useful way to think about bruxism causes when choosing practical next steps.

by Dr. Richard J. Walicki | Jan 5, 2026 | Dentistry
Oral Health in Nursing Homes: Daily Care, Diet, and the Quiet Decline No One Talks About
When families think about oral health in nursing homes, they often assume that being in a structured healthcare environment will naturally protect residents from further decline. In reality, I often see the opposite. Patients who, just a few years earlier, still had most of their natural teeth arrive at a facility and experience rapid oral deterioration—sometimes within a remarkably short period of time.
This article isn’t about blame. It’s about understanding why oral health so often declines in long-term care, even when good intentions are present, and why the causes are usually found in daily habits and systemic realities rather than in dentistry alone.
Oral health in nursing homes is currently shaped less by dentistry itself and more by daily care routines, diet, and the realities of institutional life.
Daily Habits Drive Oral Health More Than Dentistry Alone
Dentistry is episodic. Oral disease is not.
Teeth and gums are affected every single day by hygiene, diet, medications, and saliva flow. A dentist may visit a facility periodically, but plaque accumulation, inflammation, dry mouth, and dietary exposure occur continuously. When daily care falters, even the best dental intervention has limited staying power.
This is why the decline we see in long-term care cannot be understood purely through the lens of procedures or access to providers. The real drivers of decline are much more mundane—and much harder to fix.
The Reality of Daily Oral Care in Long-Term Care Facilities
Oral Care Is Often Nobody’s Job
Nursing home staff are almost universally overworked. Their responsibilities are extensive and often overwhelming, and oral care frequently falls to the bottom of the priority list. Toothbrushing, flossing, and denture care are commonly viewed as optional or cosmetic rather than medically important.
In practice, this means:
- Toothbrushing may be skipped or done inconsistently
- Dentures may remain in the mouth overnight or go uncleaned
- Sore spots, broken teeth, and loose appliances may go unnoticed until pain becomes severe
This is not usually a reflection of indifference. It is a reflection of system strain.
Some Patients Cannot Perform Oral Care—Others Can, but Don’t
An important distinction is often overlooked when discussing daily oral care in facilities.
Some residents are physically or cognitively unable to care for their mouths. Stroke, paralysis, tremors, generalized weakness, advanced arthritis, and dementia can make even basic toothbrushing impossible without assistance. These patients depend entirely on others for oral hygiene, and when help is inconsistent, decline is predictable.
Others, however, are physically capable of brushing and flossing but simply do not. This may be due to lifelong habits, depression, apathy, cognitive decline short of dementia, or a belief that oral care “no longer matters.” In many cases, these patterns long predate facility placement.
Both situations can lead to the same outcome—but for very different reasons—and both require different expectations and interventions.
Many Residents Have No History of Preventive Dental Care
For a surprising number of residents, entering a nursing home and qualifying for state benefits represents the first time in their lives they have had any access to dental care at all. Preventive dentistry may never have been part of their routine.
This often creates unrealistic expectations. Some patients assume that comprehensive dental services—crowns, bridges, root canals, surgery, even orthodontics—will now be available simply because they are in a healthcare facility. I once encountered a younger resident who was genuinely outraged to learn that braces would not be provided in a nursing home setting.
These expectations clash with reality, and the disappointment can further erode trust and engagement with even basic care.
Diet, Nutrition, and Their Role in Oral Health Decline
Institutional Diets vs Dental Reality 
Many nursing homes employ dietitians, yet the food residents consume is often poorly aligned with dental health. Soft, highly processed, carbohydrate-heavy meals are common. Sticky foods, frequent sugars, and liquid nutritional supplements can dramatically increase therisk of decay and gum disease.
These diets may meet caloric and compliance needs, but they can create an environment where oral disease thrives—especially when oral hygiene is inconsistent.
Family Food, Takeout, and Fast Food
Food also carries emotional weight. Families often bring outside food to comfort loved ones who complain about facility meals. Ambulatory residents with financial means may order takeout. Unfortunately, these foods are frequently fast food or sugary comfort items.
It’s important to be realistic: many residents have spent a lifetime eating this way. It would be unreasonable to expect those habits to suddenly change in a structured care setting. Still, the cumulative effect on oral health can be significant, especially in the absence of adequate hygiene.
Why Tooth Loss Accelerates After Placement
When reduced oral care, a cariogenic (cavity-causing) diet, medication-induced dry mouth, and limited early intervention converge, tooth loss accelerates. Teeth that might have been saved with earlier attention are instead lost to infection, fracture, or pain.
Patients should not be getting sicker simply because they are now in a structured care environment—but too often, they are.
Depression, Appetite, and the Feedback Loop
Oral health decline does not occur in isolation. Mouth pain reduces appetite. Difficulty chewing limits food choices. Tooth loss affects speech, appearance, and social interaction. Many residents become withdrawn, embarrassed, or depressed.
Depression then reduces motivation for self-care, including oral hygiene. The cycle reinforces itself, and the mouth becomes both a victim and a contributor to overall decline.
What Families Should Understand About Oral Health in Nursing Homes
Oral health in nursing homes depends far more on daily realities than on ideal dentistry.
Families should understand that:
- Daily care matters more than perfect treatment plans
- Some residents cannot physically or cognitively perform oral hygiene
- Others may choose not to, despite being capable
- Diet plays a major role, even when well-intentioned
- Rapid decline is common—but not always inevitable
This article is intended to help families set realistic expectations and understand why oral health changes so quickly after placement.
What This Article Is—and Is Not
This is not an indictment of facilities or their staff. It is not a promise that better care will prevent all tooth loss. And it is not an argument for aggressive dental treatment in every case.
It is an explanation of why oral health deteriorates quietly and predictably in many settings—and why understanding daily care and diet is the first step toward better outcomes.
Conclusion
Oral health in nursing homes is about dignity, comfort, and daily realities. Teeth do not fail overnight, and they do not fail in isolation. When daily care is inconsistent and diet is unfavorable, decline follows—even with access to dental providers.
Understanding these factors is essential. Deciding when treatment helps—and when it may not—is the next conversation families need to have.
Helpful Resources
Internal reading on ToothWiz:
External resources:

by Dr. Richard J. Walicki | Dec 6, 2025 | Dentistry
Feeling like your mouth is always dry is more than just annoying. “Dry mouth” means your saliva is not doing its normal job — and that can seriously weaken your teeth, gums, and overall oral comfort. The good news: once you understand what is causing it, there are often simple changes that bring real relief.
What is dry mouth?
Dry mouth occurs when your salivary glands do not produce enough saliva to keep your mouth comfortably moist. Saliva is your mouth’s first line of defense. It helps neutralize acids, wash away food debris, support enamel repair, and keep oral tissues healthy. When saliva is low, teeth and gums become much more vulnerable to decay, irritation, and rapid wear. For a concise medical overview, the Mayo Clinic has a helpful page on dry mouth (xerostomia).
Some people notice dry mouth only at night, others feel it all day long, and many experience a mix of both. People taking multiple medications, breathing through the mouth at night, or dealing with chronic dehydration are at higher risk.
Important: Dry mouth is common, especially with age and medications, but it is not something you have to “just live with.” Persistent dryness is a signal that your natural defenses are not keeping up.
Common causes of dry mouth
Medications
Many everyday medications list dry mouth as a side effect. These include drugs for blood pressure, depression and anxiety, allergies, asthma, pain, and urinary issues, among others. Cancer treatments, especially radiation to the head and neck, can also reduce saliva production.
If you started a new medication and soon noticed persistent dryness, it is worth mentioning this to both your prescribing physician and your dentist. Sometimes there are alternatives, dose adjustments, or supportive strategies that can lessen the impact on saliva.
Mouth breathing and sleep issues
Sleeping with your mouth open dries the tissues quickly. Snoring, nasal congestion, and untreated sleep apnea are common reasons people become mouth breathers at night. Over time, this can lead to more cavities, gum inflammation, a coated tongue on waking, and a higher risk of morning breath that does not go away easily.
Dehydration and lifestyle habits
Not drinking enough water, or consuming dehydrating substances like alcohol and caffeine, can suppress saliva flow. Add habits such as smoking or vaping, and dryness often intensifies. Long work days, frequent travel, or simply forgetting to drink enough can all contribute.
Medical conditions
Chronic conditions such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, and certain neurological issues can affect saliva production. In older adults — especially those on multiple medications — several of these factors can overlap and make dryness more severe.
Age and dental work
As people age, they are more likely to be taking medications and to have extensive dental restorations, crowns, or dentures. Less saliva plus older dental work is a risky combination: small problems can progress more quickly in a dry environment.
Why dry mouth is a serious problem for teeth and gums
Low saliva is not just uncomfortable — it changes how your mouth functions:
- Acid attacks last longer. After meals, bacteria produce acids. With little saliva to neutralize them, enamel gets eroded more quickly.
- Natural enamel repair slows down. Minerals in saliva help repair early microscopic damage to enamel. Dry mouth reduces this natural remineralization process.
- Food and plaque stick longer. Debris clings to teeth and along the gumline when there is not enough moisture to wash it away.
- The oral microbiome shifts. A dry, stagnant environment favors certain bacteria and yeast, which can cause bad breath, irritation, and infections.
Dry mouth and dentures: a major concern for older adults
If you wear full or partial dentures, saliva is more than just moisture — it is what helps the dentures stay comfortably in place. When the mouth is dry, dentures can slip, rub, and create sore spots. Many people begin wearing their dentures less often because eating and speaking become uncomfortable.
Dry mouth also increases the risk of irritation or infection under dentures. Saliva normally helps keep tissues healthy and keeps the balance of microbes under control. Without it, yeast can overgrow and cause soreness or a condition known as denture stomatitis.
Dry mouth in denture wearers is often linked to medications, which are very common in older adults. In these situations, your dentist and physician may need to work together to adjust medications or find supportive strategies to preserve saliva and tissue health.
A few simple steps can make a big difference:
- Remove dentures at night. This allows the tissues to rest and reduces irritation and infection risk.
- Clean dentures daily using products made for dentures — regular toothpaste is usually too abrasive.
- Have your dentist check the fit regularly. Poor fit causes friction, which becomes much worse when saliva is low.
- Use saliva-friendly moisturizers. Water-based gels or sprays can soothe tissues and reduce dryness during the day.
Addressing dry mouth in denture wearers is not just about comfort. It helps protect the soft tissues, reduces infections, and keeps dentures functional so you can continue to enjoy eating and smiling with confidence.
Self-check: is your dry mouth a warning sign?
Before you talk with a dentist or physician, it can help to notice patterns. Ask yourself:
- Is my mouth mostly dry at night, during the day, or all the time?
- Did this start after a new medication, surgery, or health change?
- Do I snore, mouth-breathe, or wake up with a coated tongue or sore throat?
- Do I also notice a burning sensation, white patches, or a persistent bad taste?
- Do I struggle with morning breath that does not fully clear after brushing and tongue cleaning?
These clues help your dental and medical providers decide whether your dry mouth is more likely related to breathing, medications, dehydration, systemic health, or a combination of factors.
Natural ways to relieve dry mouth
There is no single “cure” for dry mouth, but several gentle, practical steps can improve comfort and reduce damage while you address the underlying cause.
Hydrate smarter, not just more
Sipping water throughout the day is important, but plain water alone may not fully correct dryness. Adding electrolytes (without excessive sugar) can help your body hold onto fluids more effectively, especially if you are active, perspire a lot, or take diuretics. Try to limit heavy alcohol and caffeine intake, particularly later in the day, since both can worsen dryness.
Stimulate saliva gently
Chewing sugar-free xylitol gum or using xylitol lozenges can encourage your salivary glands to produce more saliva. Xylitol is not fermented by cavity-causing bacteria, which makes it safer for enamel than regular sugary mints and candies.
Choose alcohol-free oral rinses
Many over-the-counter mouthwashes contain significant amounts of alcohol, which can dry tissues even more. If you have dry mouth, look for alcohol-free rinses or moisturizing sprays formulated specifically for dry mouth. These are generally much kinder to the tissues and can provide relief without adding to the problem.
Support better breathing and sleep
If your dryness is worst at night, consider whether you might be mouth breathing while you sleep. Nasal saline rinses, a bedroom humidifier, or simple positional changes may help. If you snore loudly, wake up unrefreshed, or notice dry mouth together with headaches or daytime fatigue, it may be wise to talk with your physician about screening for sleep apnea.
Support your oral and gut microbiome
Because saliva plays a major role in balancing the microbes in your mouth, low saliva can lead to overgrowth of less friendly species. A nutrient-dense diet, stable blood sugar, and, when appropriate, targeted probiotics (oral or gut-focused) may help support a healthier oral environment. In many cases, what helps your gut and immune system will also help your mouth.
Protect your enamel in a dry environment
When saliva is low, enamel loses some of its natural protection. Brushing gently twice a day with a soft brush, cleaning between your teeth daily, and avoiding frequent sugary or acidic snacks are all essential. For a deeper dive into how enamel can be supported and repaired, you may find my article on natural tooth enamel remineralization helpful.
When dry mouth needs professional attention
Occasional mild dryness can often be managed with simple lifestyle changes. However, you should seek a professional evaluation if you notice any of the following:
- Dry mouth that persists for weeks despite good hydration and home care
- Rapidly increasing cavities, broken or chipped teeth, or new tooth sensitivity
- Sores, white patches, or a burning sensation on the tongue or cheeks
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing dry foods, or trouble wearing dentures comfortably
- Dry mouth combined with dry eyes, joint pain, or other systemic symptoms
A dental exam can evaluate your teeth, gums, and oral tissues for changes related to low saliva. Your dentist may coordinate with your physician to review medications, screen for sleep or breathing issues, or investigate possible underlying conditions.
Frequently asked questions about dry mouth
Can dry mouth cause cavities?
Yes. Without enough saliva to dilute acids and wash away food particles, cavity-causing bacteria have a much easier time damaging enamel. People with chronic dry mouth often develop cavities more quickly, especially along the gumline and around existing fillings or crowns.
Is dry mouth just a normal part of getting older?
Dry mouth is more common with age, largely because older adults are more likely to be on multiple medications and to have medical conditions that affect saliva. However, that does not mean it should be ignored. Persistent dryness is a sign that your natural defenses are compromised and deserves attention.
What is the best mouthwash for dry mouth?
In general, the best products for dry mouth are alcohol-free rinses or moisturizing gels designed specifically for dry mouth. Alcohol-based mouthwashes may feel refreshing for a moment but tend to worsen dryness over time. Your dentist can recommend products suited to your situation.
Can dry mouth contribute to cracked teeth?
Dry mouth does not “crack” teeth by itself, but it can make teeth more vulnerable. With less saliva, enamel is exposed to acids for longer periods and loses some of its natural ability to repair early damage. If you also clench or grind your teeth — especially at night — that combination of weakened enamel and heavy forces can increase the risk of cracks over time. If you have ever felt a sharp jolt when biting down or releasing pressure on one tooth, you may find my guide on cracked tooth symptoms and treatment options helpful.
Can dry mouth be cured?
Whether dry mouth can be fully reversed depends on the cause. If it is mostly due to dehydration or lifestyle factors, it may improve significantly with better hydration and habits. When medications, radiation treatment, or systemic conditions are involved, the goal is often to manage symptoms, protect teeth and tissues, and support saliva as much as possible.
Bottom line: dry mouth deserves attention
Dry mouth is common, but it is not something you have to simply tolerate. It is your body’s way of saying that saliva — your natural shield — is not keeping up with the demands placed on it. By paying attention to when dryness shows up, making targeted lifestyle changes, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can protect your teeth, support your oral tissues, and improve day-to-day comfort.
If your mouth feels dry most of the time, consider it an early warning rather than just an irritation. Listening now can save you a great deal of dental trouble later — and help you keep your mouth healthier and more comfortable for years to come.
👉 Want more support? I’m currently building a Dry Mouth Relief Toolkit that will guide you through the most common causes of dry mouth and the smartest steps to take next.
If you’d like updates — including when the toolkit goes live — follow me on Instagram or TikTok and check the link in my bio for fresh resources as they’re added. In the meantime, the tips above are a great place to start. 💧

by Dr. Richard J. Walicki | Dec 3, 2025 | Dentistry
Most people wake up with breath that does not smell very fresh. In many cases, that “morning breath” is a normal result of how your mouth behaves while you sleep. In other cases, it can be a sign that something in your mouth, sinuses, or digestive system needs attention.
What is morning breath?
Morning breath is a type of bad breath that shows up primarily when you first wake up. During the day, saliva constantly washes your teeth and tongue and helps dilute and clear away odor-causing compounds. At night, that system slows down dramatically. Saliva production drops, you are not drinking water, and bacteria have hours of quiet time to break down food debris and proteins on your tongue and around your gums. The result is a stronger mouth odor when you first open your mouth in the morning.
A mild change in breath when you wake up is extremely common. However, very strong morning breath, a bad taste, or breath that stays unpleasant for most of the day may indicate a deeper problem that is worth checking. If you want a quick overview, the American Dental Association provides a helpful article about common causes of bad breath here: ADA: Bad Breath.
What causes bad breath in the morning?
Normal nighttime changes in your mouth
Several predictable changes happen in the mouth while you sleep and contribute to morning breath.
- Less saliva. Your salivary glands slow down at night. With less fluid to wash surfaces, odor-causing molecules and bacteria build up more easily.
- Bacteria on the tongue. The surface of the tongue has many tiny grooves that can trap food particles and dead cells. Overnight, bacteria break these down and release volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs), which are responsible for much of the classic “bad breath” smell.
- Mouth breathing. Sleeping with your mouth open dries tissues out even more. A dry tongue and dry cheeks tend to smell worse because bacteria thrive in low-saliva conditions.
Habits that make morning breath worse
Everyday choices can intensify bad breath when you wake up:
- Poor oral hygiene before bed. Skipping nighttime brushing or flossing leaves more plaque, food debris, and bacteria behind, which can make morning breath stronger.
- Late-night snacks and drinks. Sugary foods, alcohol, and strongly flavored foods (like garlic and onions) close to bedtime can linger in the mouth and be broken down overnight.
- Smoking or vaping. Tobacco and some vaping products dry the mouth and add their own odors on top of bacterial activity.
- Dehydration. Not drinking enough water during the day or before bed makes it harder for your body to produce saliva at night.
When morning breath points to a bigger problem
Sometimes bad breath in the morning is stronger or more persistent because of underlying health or dental issues. These can include:
- Gum disease. Inflamed, bleeding gums harbor more odor-producing bacteria in deep pockets around the teeth.
- Untreated cavities or cracked teeth. Decay or deep structural defects can trap bacteria and food, leading to strong odors and bad taste.
- Chronic dry mouth. Some medications, medical treatments, and conditions reduce saliva all day long, not just at night.
- Sinus and throat issues. Postnasal drip, chronic sinusitis, or tonsil stones can also contribute to unpleasant smells that are especially noticeable in the morning.
- Digestive or systemic conditions. In some cases, ongoing bad breath may be related to reflux, gut imbalance, or other medical issues. These are less common than local causes in the mouth, but they do occur.
If you would like to read a concise medical overview of bad breath and its causes, Mayo Clinic has a patient-friendly summary on halitosis that many people find helpful. You can find it here: Mayo Clinic: Bad breath (halitosis)
Simple ways to reduce morning breath
You may not be able to eliminate morning breath completely, but you can often make a big difference with consistent habits. Here are practical steps that support fresher breath and better oral health overall:
- Clean your teeth thoroughly at night. Brush for two full minutes before bed and floss to remove plaque and trapped food between teeth.
- Do not forget your tongue. Gently brushing or using a tongue scraper can significantly reduce odor-causing bacteria on the tongue surface.:contentReference[oaicite:6]{index=6}
- Stay hydrated. Drinking water throughout the day and having a small amount before bed can support saliva production. Sipping water in the morning helps rinse away overnight buildup.
- Rethink late-night habits. Cutting back on alcohol, tobacco, and heavy snacks close to bedtime may improve how your breath smells in the morning.
- Support your overall health. Nutrition, digestion, and immune health all influence your oral environment. If you are interested in targeted supplements for oral and systemic wellness, you can explore options on the ToothWiz Vitamins page.
When to talk with a dentist or doctor about morning breath
It is time to seek a professional opinion if you notice any of the following:
- Bad breath that stays strong for most of the day, not just first thing in the morning.
- Bleeding gums, loose teeth, or painful chewing.
- Persistent dry mouth, trouble swallowing, or a burning sensation in the mouth.
- A bad taste that does not go away with normal cleaning.
- Signs of decay, cracked teeth, or broken fillings.
A dental exam can help identify whether the odor is coming primarily from your teeth and gums, your tongue, or nearby structures like the sinuses. If your dentist suspects that digestive or systemic conditions are contributing, they may recommend that you follow up with your physician as well.
If you are curious about other ways the mouth reflects overall health, you may also find it helpful to read about how enamel repair and support work in my article on tooth enamel remineralization.
The bottom line
Some degree of morning breath is normal and reflects how your mouth behaves overnight. However, strong, persistent, or worsening odor is not something you have to simply tolerate. Paying attention to hydration, tongue cleaning, and consistent home care can make mornings more pleasant, and a thorough evaluation can rule out (or address) gum problems, cavities, and other causes.
If you are concerned about how your breath smells when you wake up, do not be embarrassed to bring it up. It is a common concern, and a thoughtful conversation with your dental team can help you understand what is going on and what options you have to improve it.










